
IEA Forecasts 32% Growth in Coming Years for Biogas Sector
On January 11th, the International Energy Agency (IEA) published its annual report: “Renewables 2023” which specifically delves into the deployment of renewable energy at the country level until 2028. This year’s report included a special section dedicated to biogas and biomethane.
Following the war in Ukraine, policy changes for energy security, the pressing necessity to address climate change, and favourable market conditions, have increased the focus on biogas as a sustainable and readily deployable alternative to natural gas.
Over the last six years (2017-2022), the biogas sector experienced a growth rate of 19%, reaching 445 TWh in 2022. The production was concentrated in European, American, Chinese and Indian markets – with Europe responsible for almost half of this production and Germany alone contributing 20%. For the near future, the IEA’s Net Zero Scenario forecasts a strong growth rate of 32% between 2023 and 2028. This projection aligns with a broader trend identified in the IEA’s Energy Outlook 2023 of an increasing global interest in the sector, especially in biomethane.
Charlotte Morton OBE, WBA Chief Executive commented:
This is a huge milestone for our industry. Not only does the IEA recognise the role our industry can play as a solution to the world’s current economic and environmental crises, it anticipates the sector growth rate to accelerate from 19% in 2017-2022 to 32% in 2023-2028.
The Anaerobic Digestion sector is particularly well placed to help meet the Global Methane Pledge commitments made by over 150 countries since its launch in 2021. Our research (1) has shown that fully deployed, the biogas and biomethane sector could deliver 50% of the Pledge. The IEA’s forecasts and growing commitment from governments indicate that we are on the right path. The sector, however, requires strong policy support to realise multifaceted benefits of AD.
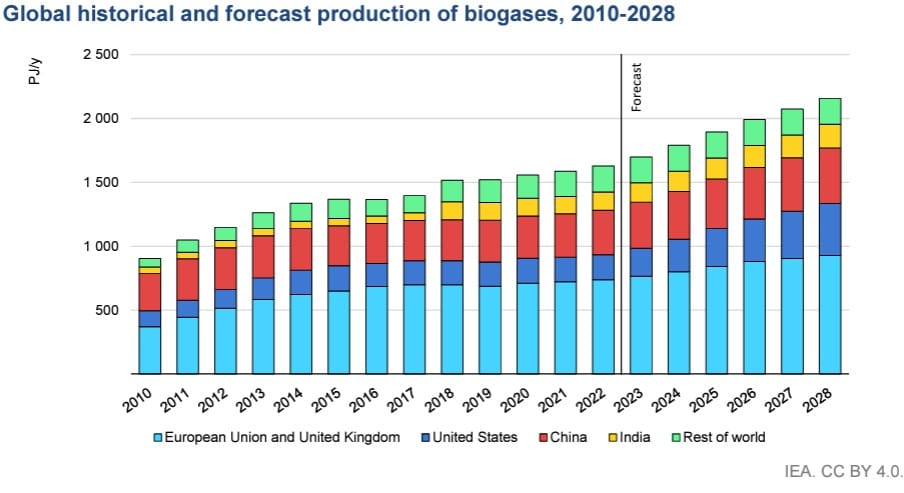
Figure 1 IEA’s projection for Biogases (Source: Special section: Biogas and biomethane, IEA’s renewables 2023)
The key catalyst for future growth is underlined by strong policy support by the government in more than 13 countries. For the renewables sector at large, government polices focusing on fixed tariffs and premiums, and auctions are leading the way. From the perspective of countries, the sector for now will be driven by mature markets of Europe, the USA, and Canada reaping benefits from existing infrastructure, fruits of past policies, and expertise; India and China in comparison will have to work on the feedstock supply chain and infrastructure within the next five year to see accelerated growth in future forecasts.
Country-specific Market
Due to the diverse nature of the biogas and characteristics of energy systems, countries have significant variations in terms of usage. A large proportion in Europe and the USA are dedicated to heat and electricity closely followed by injection into natural gas grid and road transportation respectively. In comparison India and China see more use in residential, commercial, and public service.
This trend is set to shift in the coming years as both countries tackle rising energy demands and set ambitious decarbonisation goals. China since 2019 has been investing in the installation of large-scale bio-natural gas (BNG, biomethane) projects ((>10 mcm/year)) in the hope of integrating urban and rural waste to produce electricity and gas. India is following a similar approach to transit from small household AD plants to industrial plants for transport and industrial fuels. Policies like STATA, one Nation One Gas Grid, and the National Biogas Program are backing the production of biogas and biomethane through tariffs, financial aids, and other supports aiming to increase the share of natural gas to 15% by 2030 (For detailed analysis on Indian Policy Landscape, check out WBA’s Market Report).
Governments in the European markets are shifting to competitive models and cost reductions alongside a shift from CHP to more flexible use of biomethane. As seen Biomethane’s role in vehicle fuel has been growing, constituting around 20% of gas consumed by gas-fueled vehicles in 2021. Additional focus is also being directed toward energy-neutral feedstock, with Germany shifting from energy crops after ten years of support and France banning it altogether.
The UK’s production from landfill gas has seen a reduction of 46% in the last 12 years. This reduction can be linked to the successful management of organic waste, anaerobic digestion specifically has played a big role here digesting around 46 million tonnes of organic material each year (ADBA 2024). The number of anaerobic digestion plants within the last 12 years has more than tripled with an average growth rate of 18.4% per year (as per ADBA’s analysis).
In the USA, the transport sector and support scheme have bolstered the growth of the sector. Recently, the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) set annual volume obligations on RNG intending to double biomethane supplies in the next three years. States like California and Washington are further developing their support schemes that add to the financial benefits of RFS. The current policies such as investment tax credits, production tax credits, and hydrogen tax credits want to incentivise the production of biomethane from landfill gas, a low-cost production option. As of now, biomethane has a share of 48% in gaseous transport fuels, the largest in the world.
The industry celebrates the recognition being given to the biogas sector for its contribution towards a sustainable future and circular economies. Our research shows that when fully deployed Biogas could deliver 50% of the Global Methane Pledge. The role of anaerobic digestion in mitigating methane emissions from agriculture and livestock management, food waste management and landfills and its impact on 9 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals2 are increasingly being recognised. This is putting the sector in a strong position to rapidly produce a net cooling effect, as the world continues long-term CO2 reduction. However, extensive capital mobilization, both in terms of infrastructure and financial incentives and supporting policies is imperative to achieve the growth forecasts made and realise the full potential of the anaerobic digestion industry.

